Proof of Identity is a very important concept throughout the cybersecurity world. It is an idea that helps maintain the security and integrity of digital systems. As such, it can be applied in a variety of contexts, which we will explore in further detail below.
What Is Proof of Identity?
In a cybersecurity context, Proof of Identity refers to the process of verifying and validating an individual’s identity.
This can be applied across many use cases online, from digital transactions to gaining access to online resources. All in all, the point of Proof of Identity is to ensure that only rightful and authorized users are granted access privileges and that unauthorized access is prevented.
On a larger scale, Proof of Identity is used to protect against serious crimes like identity theft and fraud.
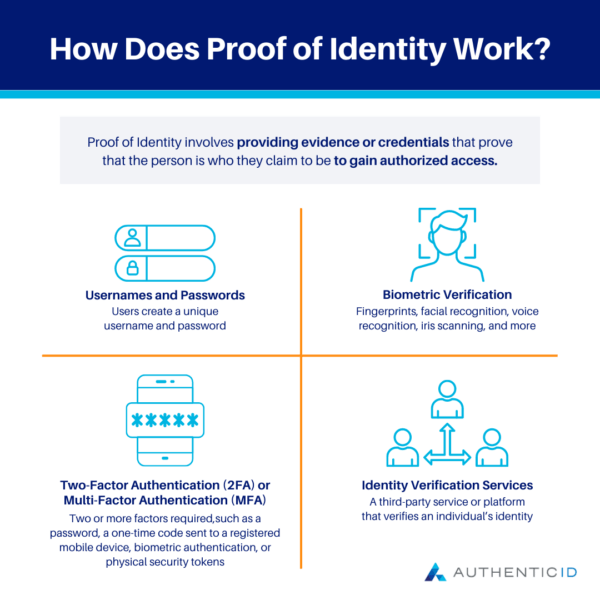
How Does Proof of Identity Work?
Depending on the application or platform, and its governing guidelines, Proof of Identity can look very different from case to case. In general, Proof of Identity involves providing evidence or credentials that prove that the person is who they claim to be to gain authorized access.
To get a better idea of this concept, here are some of the ways that Proof of Identity can work in practice.
- Usernames and passwords: the most basic form of Proof of Identity; users create a unique username and password to access online accounts or systems
- Biometric Verification: relies on unique biometric factors like the user’s fingerprints, facial recognition, voice recognition, iris scanning, and more to verify their identity
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): a method that relies on two or more factors to verify a user’s identity; factors can include a password, a one-time code sent to a registered mobile device, biometric authentication, or physical security tokens
- Identity Verification Services: a third-party service or platform like a Digital Identity Wallet that verifies an individual’s identity on behalf of the platform or app they are trying to access; the user must first go through the verification process with the service provider by providing supporting documentation to establish identity authenticity
Benefits of Proof of Identity
The benefits of proof of identity are probably pretty straightforward. However, let’s take a more detailed look at some of the advantages it can provide.
1) Better Security
The primary reason why Proof of Identity is utilized is for enhanced security since it helps to establish the authenticity of a user’s identity. This keeps bad actors or unauthorized users from accessing sensitive information, systems, or resources.
As we’ve already discussed, Proof of Identity works to prevent identity theft and other related crimes, which can include adverse incidents like data breaches and other malicious events.
2) Strong Access Control
Another great benefit provided by Proof of Identity is the control over user access. App administrators can enable Proof of Identity to ensure that users are granted appropriate system access based on their roles and privileges.
Supporting security measures even further, Proof of Identity helps make sure that only the rightful parties gain access to sensitive information or critical systems.
3) Trust and Transparency
Proof of Trust can also build trust among users that their personal information and data that is stored in different systems and applications is protected from unauthorized users.
Plus, once inside the system, it provides reassurance that the individuals they are interacting with are vetted and genuine as well. Put together, this works to create confidence in online transactions, e-commerce, and digital services.
4) Regulatory Compliance
Across different jurisdictions, new regulations surrounding user identity verification and data privacy rights have emerged. As a result, Proof of Identity becomes even more applicable at helping organizations comply with these regulatory requirements and ensure only authorized users are granted access to protected information.
Otherwise, organizations could face legal consequences, fines, and reputational damage in the case of non-compliance.
5) Secure Online Transactions
Lastly, Proof of Identity can help facilitate secure online transactions, something that is becoming more and more necessary today as the world continues to move online.
This can be applied in the context of e-commerce, online banking, digital payments, and more. In each of these cases, Proof of Identity helps support the integrity and security of the transactions. With this in mind, Proof of Identity can help reduce the risk of fraud or financial loss from malicious actors gaining access to sensitive financial data that may be stored in online accounts.
Potential Risks with Proof of Identity
Overall, Proof of Identity is instrumental in how we navigate the online world today. While it can be effective at helping to prevent fraud and other negative occurrences, it is not foolproof. Here are some potential risks to look out for regarding Proof of Identity.
- Weak passwords: cybercriminals’ tactics are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making simple password-username combinations easier to compromise than other forms of Proof of Identity; make your passwords complex, regularly change your password, and don’t utilize the same password for all online accounts
- Identity theft: if Proof of Identity information falls into the hands of bad actors, it could be used for identity theft; perpetrators could impersonate the individual and open up bank accounts or engage in illegal activities with the stolen identity
- Social engineering attacks: online attackers can manipulate individuals into revealing or providing Proof of Identity information; be aware of scam phone calls, phishing emails, or impersonation attempts asking you to disclose personal information
- Data breaches: organizations are always susceptible to data breaches; if attackers gain unauthorized access to their systems, it could lead to fraud, identity theft, and other crimes
- Insider threats: insiders pose a serious data security risk; insiders like employees or contractors may have privileged access to Proof of Identity information, and can misuse or leak the data for their own personal gain

