A privileged access management (PAM) tool is a solution that mitigates any risk of privileged access via monitoring, detecting, and/or preventing unauthorized access to system resources.
As an organization expands and adds new users with new permissions over the years, they can quickly lose sight of all accounts that have elevated privileges and access to sensitive data.
At the same time, incidents of cyber attacks are on the rise, posing a serious threat to organizations in all industries. This is due to many factors, but right-sizing account permissions and gaining more control over who has access to what, and when, is an important step that IT leaders need to take to safeguard their systems.
Continue reading below to learn more about how Privileged Access Management solutions are helping to solve this problem and the numerous advantages they provide.
What is Privileged Access Management?
Certain accounts in an organization’s IT infrastructure will have elevated, or privileged, access to special systems, administrative features, and sensitive information that other accounts do not have.
Thus, Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a set of policies, protocols, and technologies that help organizations manage and secure privileged accounts within their systems. This concept can also be referred to as Privileged Account Management, Privileged Identity Management, or Privilege Management.
The primary goal of Privileged Access Management is to reduce the potential risks that privileged accounts pose by imposing strong controls, monitoring account activity, and mitigating security threats. In return, organizations gain more visibility and transparency over users’ permissions and what they are accessing.
As a result, PAM can help safeguard the organization against bad actors and reduce the potential attack surface in their tech stack.
Why Is Privileged Access Management Needed?
Privileged users and accounts can pose a number of threats to organizations, which is one of the main reasons why PAM is necessary.
By definition, privileged users have access to high-level systems, critical applications, and sensitive information that the typical user does not. As such, the threat that a bad actor gains access to one of these accounts, or an internal party has malicious intentions on their own, is a major risk to organizations.
Plus, as we discussed earlier, as an organization grows and adds new users, programs, and devices, teams share passwords to certain programs, and other complexities, leaders can easily lose visibility over access privileges.
This has possible implications for compliance issues, audits, and forensic investigations in the case of an attack. In other words, if an organization doesn’t have clear control over their privileged accounts, it can be difficult to track down where the attack came from, and who is the responsible party.
How Does Privileged Access Management Work?
Privileged Access Management relies on a few key cybersecurity principles to function properly. Primarily, PAM functions with the concept of least privilege, meaning users and accounts are only granted as much privileges as are required to complete their tasks, and nothing more.
Here are some of the main aspects and best practices of Privileged Access Management:
- Privileged Account Discovery: organizations identify and catalog all privileged accounts within their systems spanning various platforms, databases, applications, and devices
- Access Control and Authentication: PAM enforces strict access controls and authentication methods for privileged accounts to ensure only authorized users gain privileged account access (including Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), password policies, etc.)
- Session Monitoring and Recording: organization can track and log activities performed by privileged users during their sessions for even more visibility; this can prove beneficial in forensic analysis, audits, and fraud detection
- Credential Management: part of PAM is managing privileged account credentials like passwords and enforcing policies to ensure they are being updated and changed frequently; this prevents the risk of using compromised or weak passwords to mitigate possible theft or unauthorized use
Keep in mind that Privileged Access Management can look different for each individual organization depending on their unique operational needs, the security measures that are already in place, and other factors.
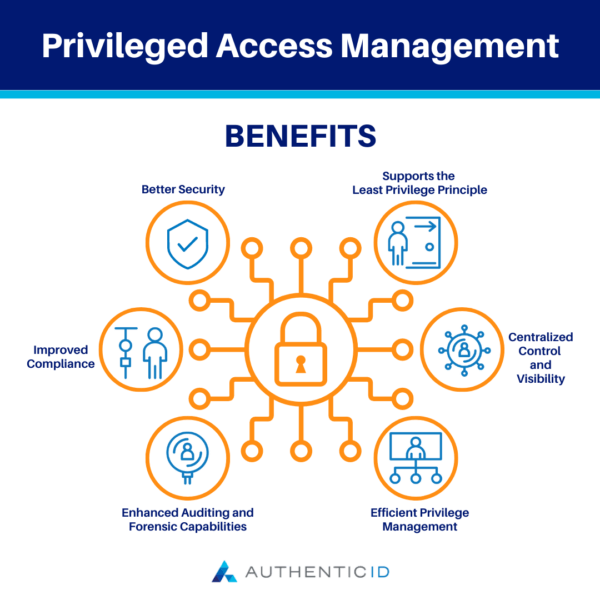
What are the Benefits of Privileged Access Management?
As you could gather, there are plenty of benefits that Privilege Access Management offers organizations. Let’s highlight some of the largest advantages that it brings.
1. Better Security:
The number one benefit of Privilege Access Management is the enhanced security it offers organizations. The overall goal of PAM is to mitigate the risk of security incidents from privileged account misuse either by insiders or attackers.
By implementing stronger access controls, authentication policies, and session monitoring, PAM helps reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data.
2. Supports the Least Privilege Principle:
Privilege Access Management supports the principle of least privilege by only granting privileged access to users when appropriate and necessary. As a result, organizations enjoy a reduced attack surface that can limit the potential damage caused by compromised accounts or misused privileges.
3. Improved Compliance:
There are many regulations and industry standards and guidelines out there that require organizations to have controls in place for managing privileged accounts–including GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and others.
Thus, Privilege Access management helps organizations meet compliance requirements through auditing, reporting, and access controls that demonstrate appropriate privilege management.
4. Centralized Control and Visibility:
Organizations also gain a centralized platform for managing and monitoring privileged accounts when they’ve implemented Privilege Access Management.
They can gain visibility into privileged access activities and track and audit these behaviors, generate detailed reports, and flag possible suspicious activity. Aside from better transparency, it helps organizations make more timely responses to security incidents.
5. Efficient Privilege Management:
When Privilege Access Management is in place, it becomes easier for organizations to revoke or grant privileged access to users when necessary. They can implement and automate approval mechanisms, credential management policies, and more for better security.
Overall, PAM can help organizations streamline their operations and reduce the administrative burden that’s associated with managing user privileges.
6. Enhanced Auditing and Forensic Capabilities:
Organizations that have implemented PAM solutions gain more robust auditing and forensic investigation capabilities.
When in place, PAM solutions capture detailed logs of privileged access activities, offering a detailed view of keystrokes and command history during these sessions. So, in the case of an attack or breach, it’s much easier for organizations to discover the source of the incident and respond more quickly.

