Biometric verification technology utilizes physical characteristics, including but not limited to fingerprint, facial scan, retina scan, etc. to identify someone. Biometric technology is increasingly used in security processes to authenticate and re authenticate users to ensure a user is who they say they are.
What is Biometric Verification?
Biometric verification is a way for individuals to be identified based on one or more of their unique biological characteristics. This method is often viewed as a more secure, efficient, and reliable way for individuals to be verified, as opposed to a PIN or password, which can be more easily compromised or replicated.
Biological traits used for verification can include voice recognition, written signatures, fingerprints, DNA, iris or retina patterns, and others.
To set up biometric verification, the process is typically the same no matter which trait the system relies on. An authorized individual’s biometric marker is recorded and stored in a database, which can then be compared against future access attempts.
When a person attempts to log in to a system, device, or account, a new record of the chosen biological trait is recorded and compared against the stored version. If the two samples match, the individual’s identity is confirmed and they are granted access.
What are the Different Types of Biometric Verification?
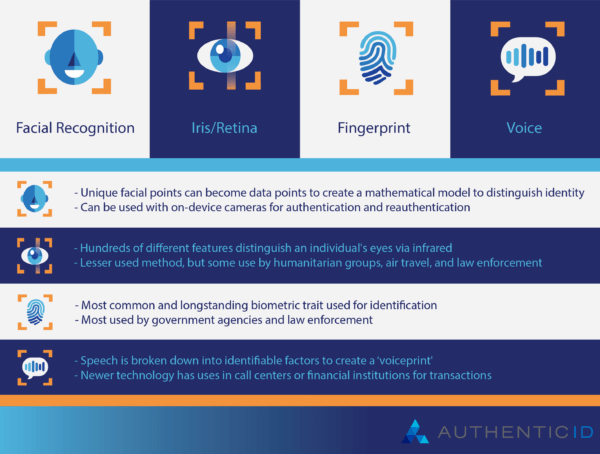
Biometric verification can use a number of markers to verify the identity of users, including the following:
- Facial recognition
- Iris/retina
- Fingerprint
- Voice
Let’s take a deeper look at each of these biometric traits and how they’re effective at identifying individuals.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition is one of the more common uses of biometric verification today. When facial recognition is utilized, the unique map of an individual’s facial features will be stored to verify their identity in the future.
Unique points on the face like height and width, distance between pupils, depth of features, and thousands of other metrics can be tracked. These data points are then used to create a mathematical model that distinguishes the identity of individuals.
Iris/retina
Each person’s retina and iris patterns are extremely unique and can vary greatly between individuals, even if it doesn’t appear that way from afar. In fact, a typical iris scanner can recognize hundreds of different features that distinguish one person’s eye from another.
Similar to a fingerprint, they can act as individual markers to identify people, making them a great trait to use with biometric verification.
Fingerprint
Probably the most common and long-standing biometric marker is fingerprint identification. It is highly reliable, as there is a one in 64 trillion chance that you share a fingerprint with someone else. Plus, it’s hard to replicate a fingerprint with accuracy that will pass modern biometric verification systems.
Its historical success record also supports its continued use, as it’s been widely relied upon by government agencies and law enforcement for decades.
Voice
While not a physical feature, voice recognition is a good example of the vast array of biometric markers that can identify someone, aside from physiological traits.
The science behind voice recognition technology is that programs can break down a person’s speech into a number of identifiable factors to create a ‘voiceprint,’ much like a fingerprint. This voiceprint can include features like accent, pitch, frequency, speed, tone, and more to distinguish one person from another.
What are the Benefits of Biometric Verification?
There are many reasons why organizations are implementing biometric verification into their security processes over other verification programs:
1. Convenience
The ease with which users can verify their identities with biometric verification is one of the main benefits of utilizing this technology. Although the back end of such systems can be quite complex, it likely doesn’t appear this way to end users.
Rather than needing to remember a different password for each program or troubleshoot failed login attempts, users can quickly and easily be granted access to their authorized programs and systems by simply scanning their fingerprint, face, eyes, or other features.
2. High levels of security
Possibly the most important benefit of biometric verification is the high level of security and assurance that it provides.
Biometrics allows programs and organizations to verify the identity of users with real, tangible data that must be provided in real-time. It is something that each person in the world has that can also clearly distinguish them from others.
Data breaches of online programs, websites, and databases are all too common. Information like passwords and PINs can easily be compromised and fall into the hands of bad actors or cybercriminals, who can then utilize these traditional authentification methods by acting as the authorized user and inputting this compromised data.
Replicating traits like face patterns, iris or retinas, or fingerprints is nearly impossible with today’s technology. So, it’s very unlikely that a wrongful user will be able to grant access with falsified biometric markers.
3. Non-transferable
Each person has their own unique set of distinguishable biometric traits. These features are hard to replicate, fake, or steal from others, further enhancing the security of such programs.
At the time of a log-in attempt, the biometric marker must be provided. It’s not something that can be shared online or accessed by multiple individuals in different locations.
Thus, there is no ‘password-sharing’ that can occur with biometric verification. A successful log-in attempt cannot occur without having the authorized user there in person during the log-in process.
Common Use Cases of Biometric Verification
Many industries rely on biometric verification. Its use is only becoming more popular as the technology becomes more widely available and with the help of cloud-based storage that can store large amounts of data more efficiently.
Because of the high levels of security biometric verification provides, it is particularly useful in industries that involve the collection, storage, and use of sensitive data.
Here are some of the industries that frequently utilize biometric verification, and how they leverage this technology:
• Financial services: voice recognition and other biometric data are used to identify phone callers before discussing account details
• Law enforcement: use fingerprints, DNA, facial recognition, and other biometric traits to trace and track individuals within the criminal justice system
• Government: increased use of facial recognition and other biometric markers for voter registration, DMV purposes, and more
• Healthcare: these facilities can use biometric markers to identify patients
• Travel industry: leverage facial recognition, fingerprints, and other data for passports, registered traveler programs, and more
• Workforce solutions: use of fingerprints, iris or retina scanning, facial recognition, and other markers to permit user access to an organization’s systems or assets
Given that biometric verification is still an emerging technology, it use cases will only continue to expand in the coming years.
With this in mind, the above examples are not nearly an exhaustive list of all the ways that this technology is utilized currently, though they can give you a good idea of how entities today are leveraging biometrics for better efficiency and accuracy with identity verification.

